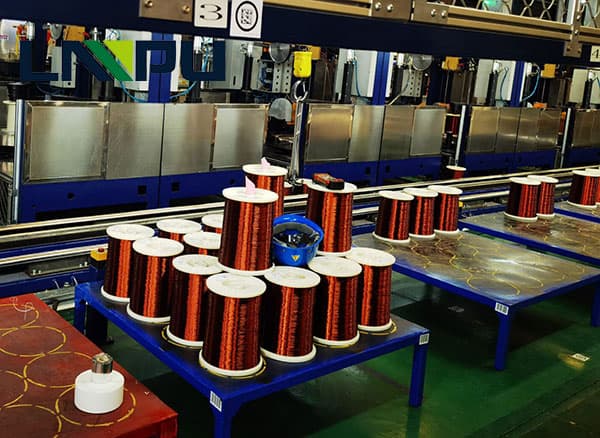
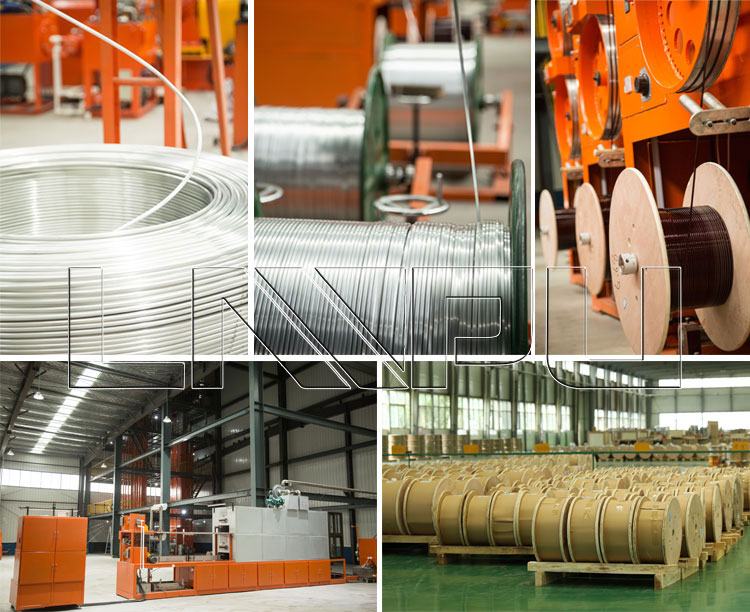
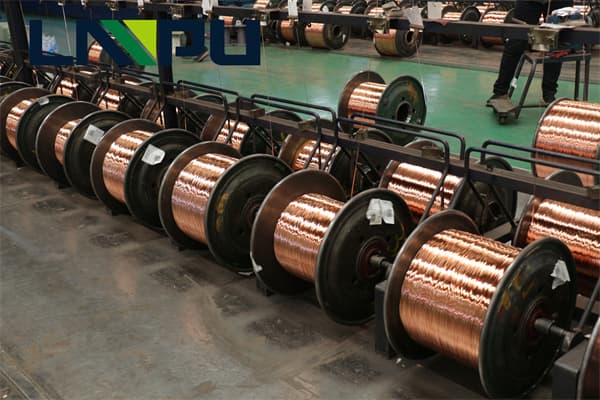
Various properties of copper wire
1. Conductor resistance ¡ª The resistance of a conductor is proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area.
2. Conductivity¡ªBased on the resistance 1/58ohm (0.017241 ohm) of a standard soft copper wire with a length of 1m and a cross-sectional area of 1mm2 at 20¡æ, it is called 100% conductivity. The greater the resistance, the lower the conductivity, and the two are inversely proportional.
3. Bending resistance¡ªfix one end of the single wire, add weight to the other end to make it vertically downward, and then bend it back and forth 180 times until the wire breaks. The more bending times, the stronger the bending resistance.
4. Tensile breaking force¡ªthe maximum load weight or force applied to the specimen to break it during a tensile test.
5. Tensile strength¡ªthe breaking force per unit area to bear when the sample is broken during the tensile test.
6. Elongation ¡ª the ratio of the length of the sample after being stretched until it breaks to the original length at the specified standard distance. Conductors have different impedances at different temperatures.
Generally, 20¡ãC or 25¡ãC is the standard. The higher the temperature, the greater the impedance.