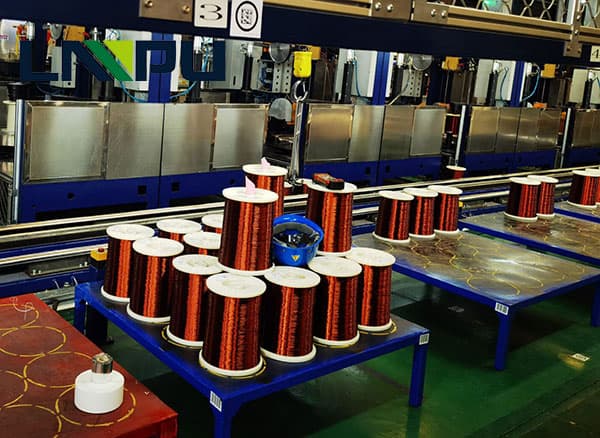
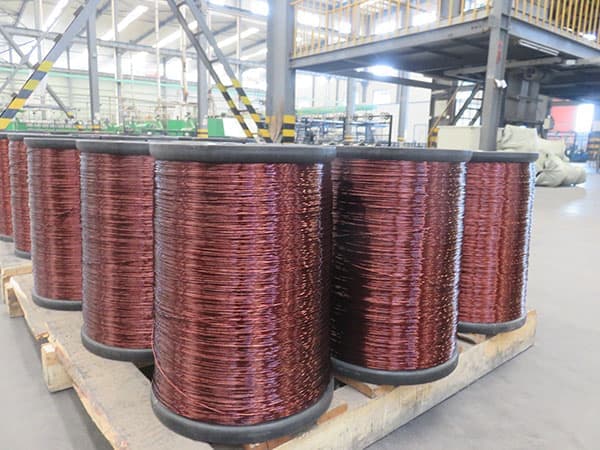
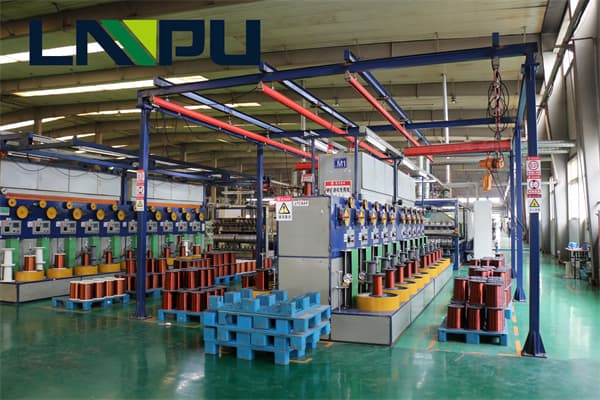
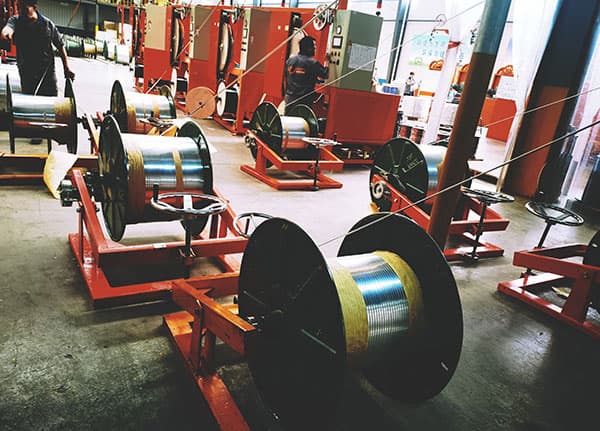
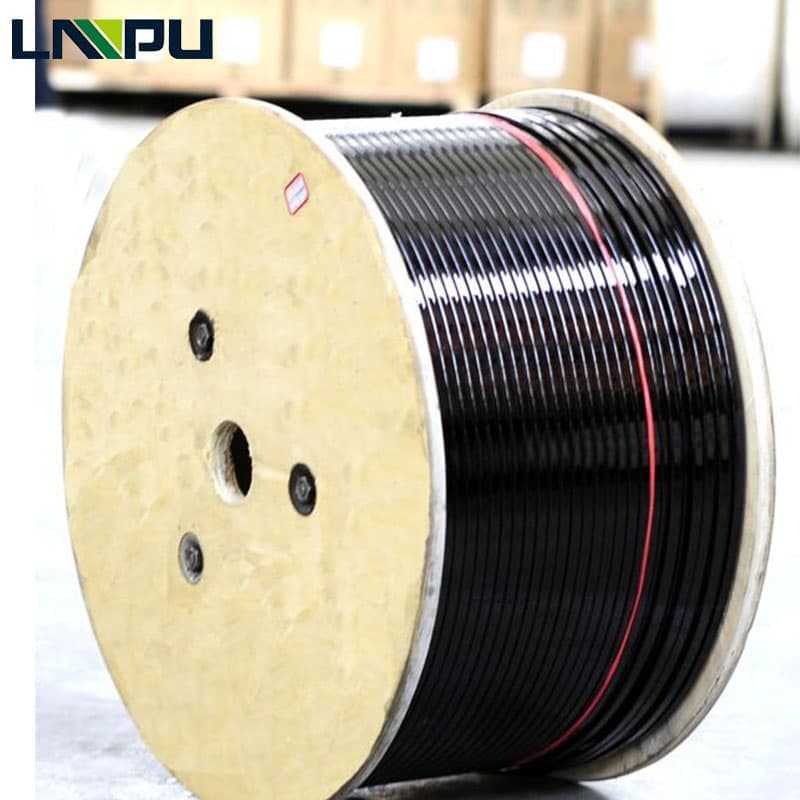
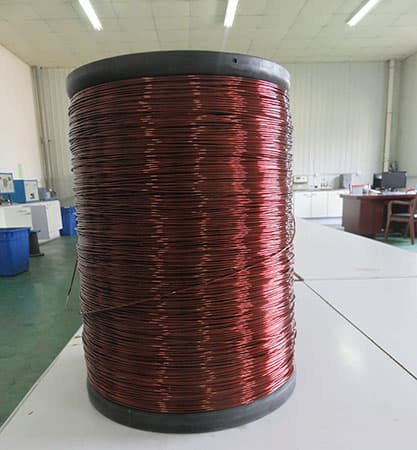
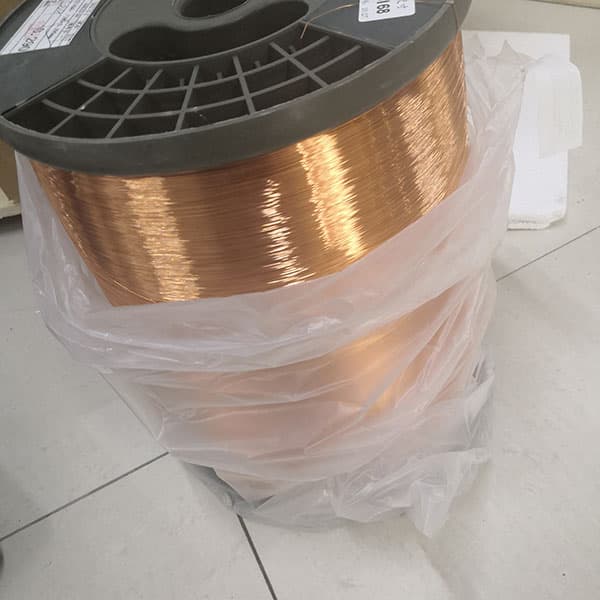
Thermal resistance of super enamel wire
Heat resistance refers to the properties of a substance that can maintain its excellent physical and mechanical properties under heated conditions. The highest use temperature of commonly used materials to characterize. There are different standards and test methods for different materials. Such as plastics are generally expressed by Martin heat-resistant temperature. The coating industry uses a blast constant temperature oven or a high temperature furnace. After it reaches the specified temperature and time, the surface condition of the paint film is inspected, tested, or other properties such as impact, bending, water immersion, salt spray test, etc., and then before and after Test data representation. All coatings used in higher temperature occasions must use heat resistance as an important technical indicator of the coating film
Heat resistance grade
The insulation life of electrical products is affected by many factors (such as temperature, electrical and mechanical stress, vibration, harmful gases, chemical substances, humidity, dust and radiation, etc.), and temperature is usually the aging of insulation materials and insulation structures The dominant factor. Therefore, there is a practical and world-recognized classification method for heat resistance, that is, the heat resistance of electrical insulation is divided into several heat resistance grades. Each heat resistance grade and the corresponding temperature value are as follows:
Heat resistance grade temperature, ¡æ
Y 90
A 105
E 120
B 130
F 155
H 180
H+ 200
HC 220
250
If the temperature exceeds 250¡ãC, the heat resistance level shall be set according to the interval of 25¡ãC.
The heat-resistance grade marked on an electrical product usually indicates the highest temperature that the product can withstand when it reaches the expected service life under the rated load and other specified conditions. Therefore, in electrical products, the insulation temperature used at the highest temperature should not be lower than the temperature corresponding to the product’s heat resistance class.