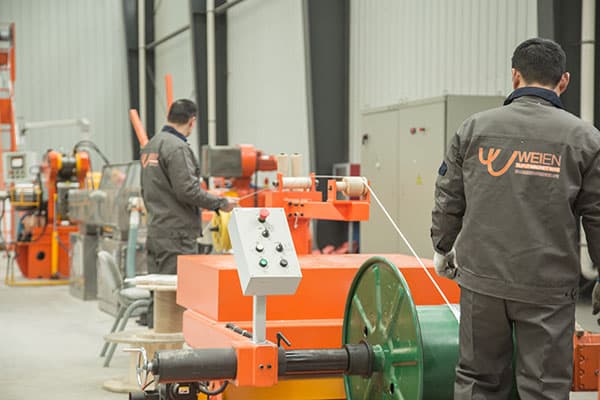
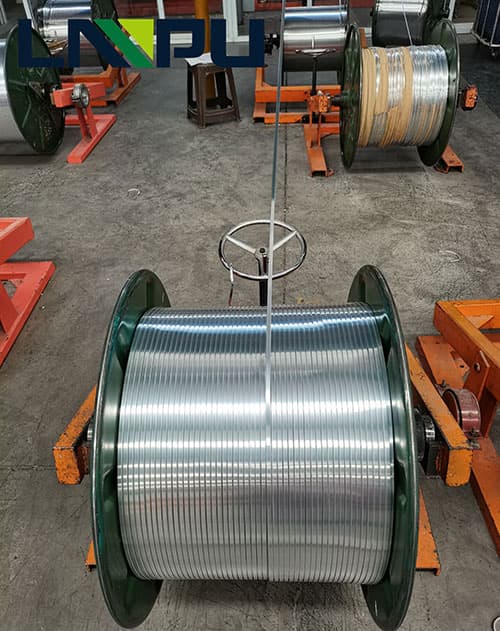
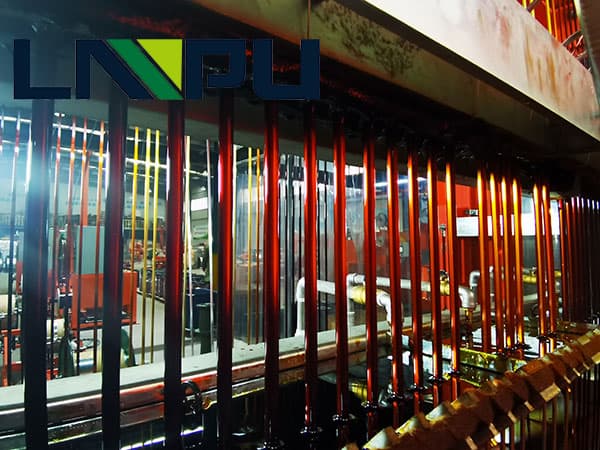
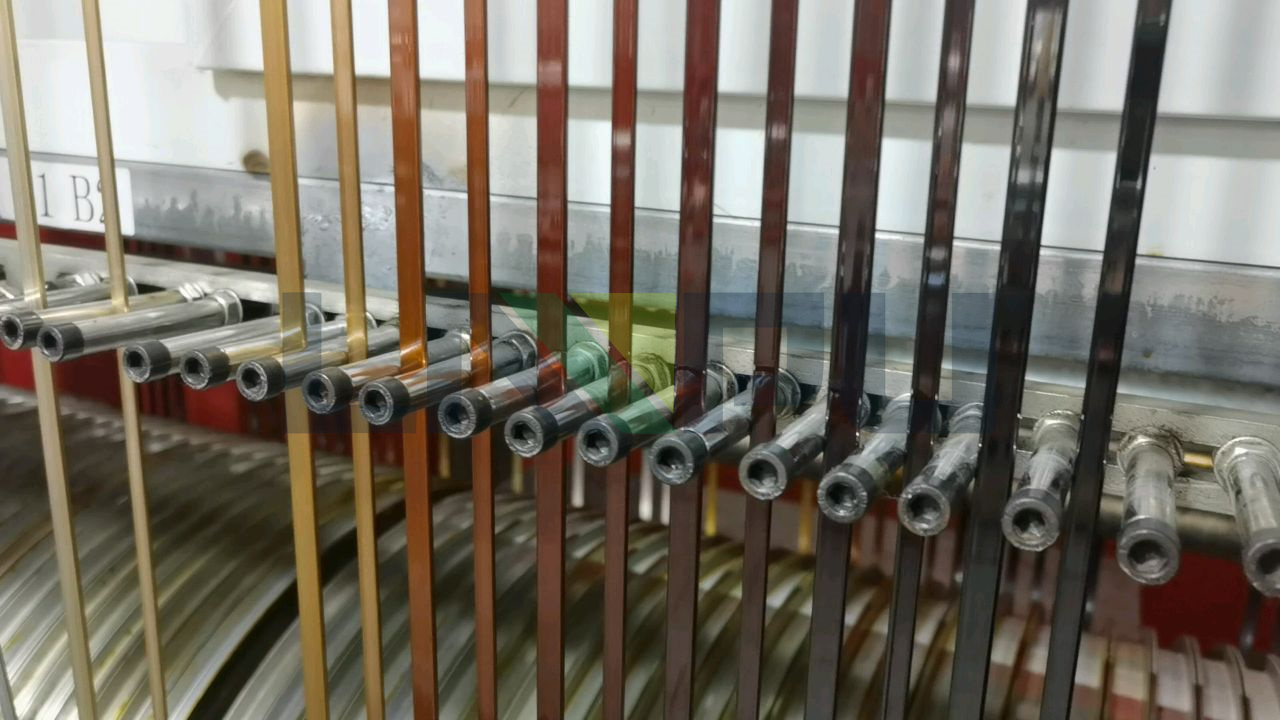
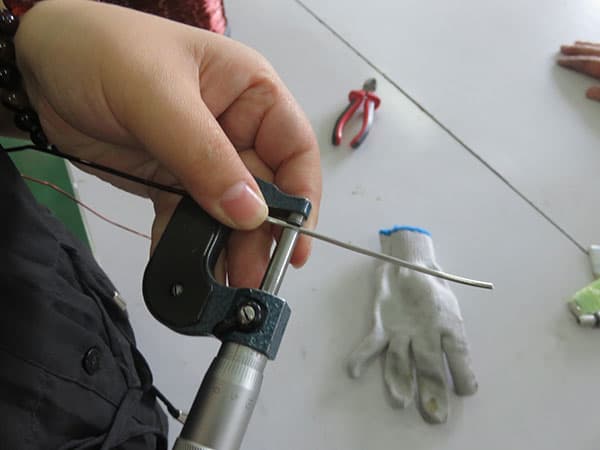
Enameled wire characteristic test
¡ñConductor resistance. Measured with a conductor resistance tester, and then changed to the value at 20¡ãC for comparison.
¡ñ Dielectric breakdown voltage. Twist two enameled wires, apply voltage between their conductors, and judge by the breakdown voltage of the paint film. The performance is analyzed and judged by two tests of normal state and cold state breakdown voltage.
¡ñContinuity of paint film (pinhole). Check the paint film pores with a certain length of test material. This item is tested by the high pressure paint film continuity tester.
¡ñFlexibility (flexibility). When winding or elongating, judge whether the paint film is cracked or whether pinholes are generated.
¡ñAdhesion. The paint film should be cracked when it is stretched rapidly.
¡ñAbrasion resistance. When the paint film is abraded by the abrasion tester, the number of times to see the conductor or the abrasion damage value is measured by the scratch resistance paint tester.
¡ñAging resistance. When heated under specified conditions, analyze whether the paint film has pinholes or insulation breakdown voltage value.
¡ñ softening resistance. Heat the crossed enameled wires under the specified conditions, and check whether there is a short circuit or a short circuit temperature after the power is turned on. Or twist two enameled wires and heat them under specified conditions, depending on whether the paint film is abnormal.
¡ñThermal shock resistance. When stretching or winding, heat under specified conditions to see if the paint film is cracked.
¡ñSolvent resistance, chemical resistance and oil resistance. When immersed in solvents, chemicals or insulating oils, the state of the paint film is indicated by the nail method or the pencil method.
¡ñStraight welding. According to the specified conditions of temperature, solder, and whether the solder is evenly attached.